EU high-tech trade: exports up in 2023
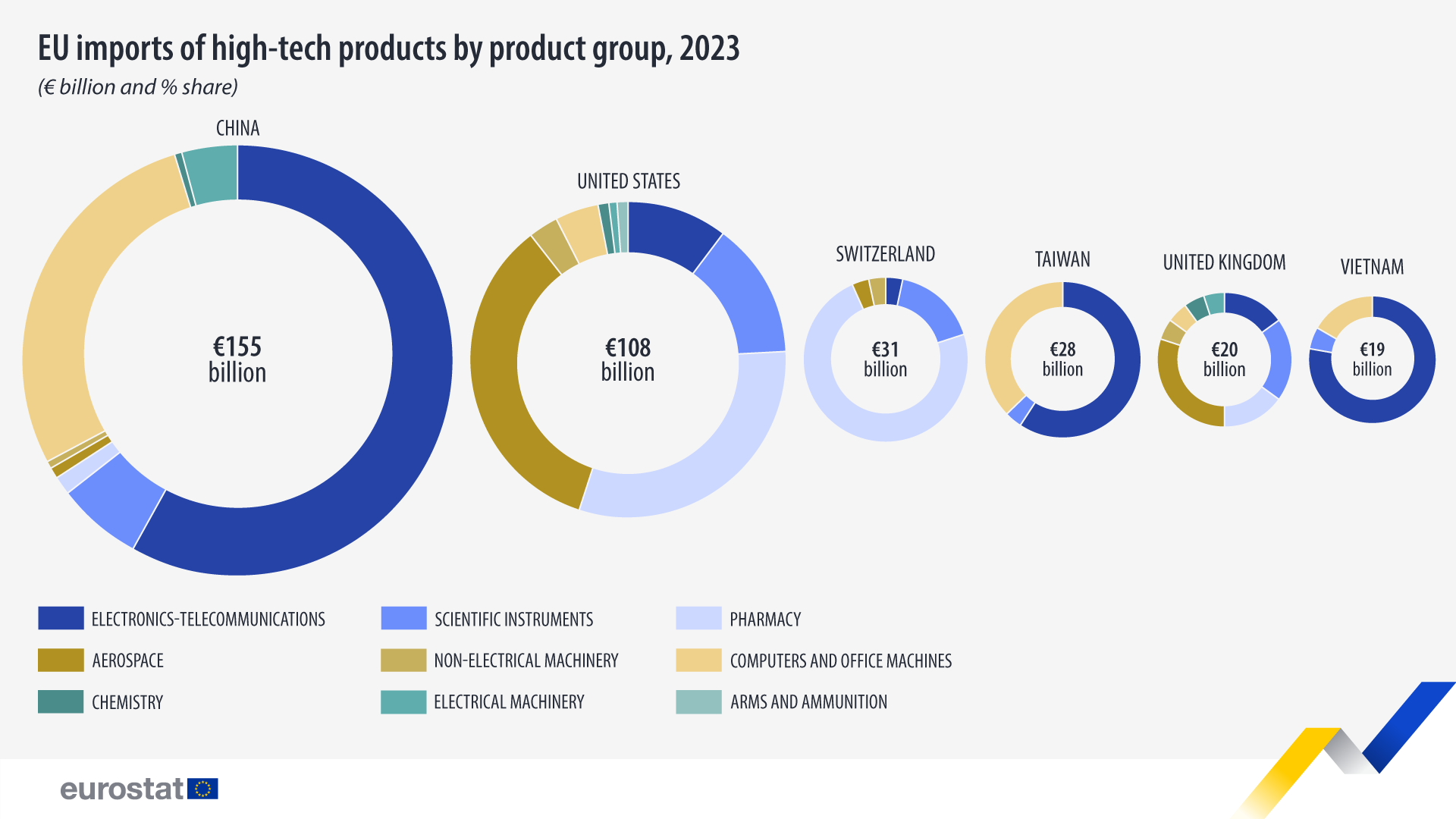
Over half of the EU’s high-tech imports in 2023 came from China (32%; €155 billion) and the United States (23%; €108 billion), with other top partners being Switzerland (7%; €31 billion), Taiwan (6%; €28 billion) and the United Kingdom and Vietnam (each 4%; €20 and €19 billion respectively).
Electronics-telecommunications accounted for the largest share of high-tech imports from non-EU countries (39%), for which China was the largest partner. Computers and office machines as well as pharmacy both accounted for 15% of high-tech imports, most of which came from China and the United States respectively.
Source dataset: DS-018995; Eurostat extraction
Electronics-telecommunications made up the largest share of imports from Vietnam (73% of high-tech imports from Vietnam; €14 billion), Taiwan and China (each 58%; €16 billion and €89 billion, respectively).
For Switzerland, the largest category was pharmacy (70% of high-tech imports from Switzerland; €22 billion).
For the United States (35%; €37 billion) and the United Kingdom (30%; €6 billion), it was aerospace.
Pharmacy comprised 30% of high-tech exports
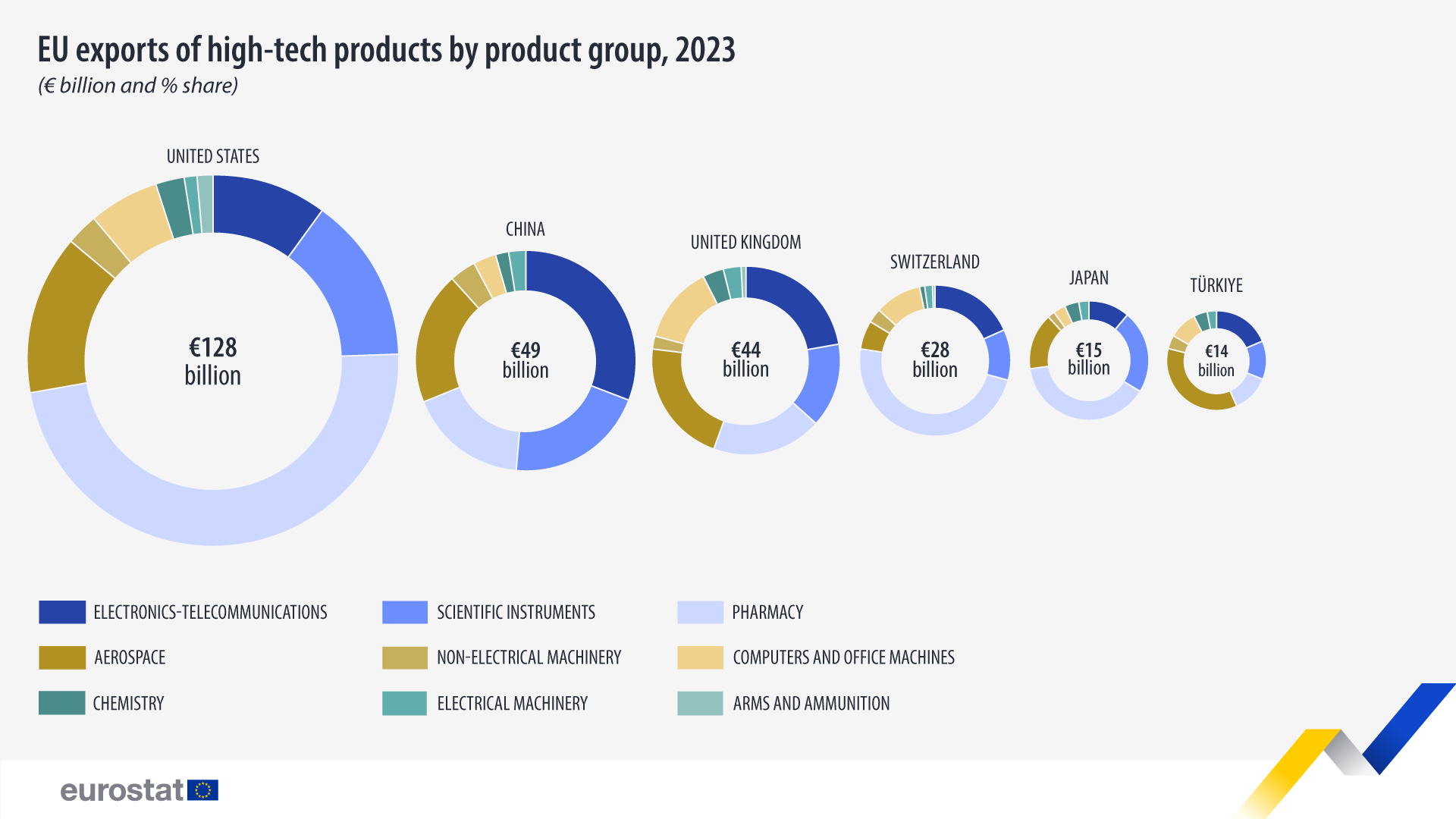
In 2023, the United States was the top trading partner (28%; €128 billion) for high-tech exports to non-EU countries. China followed (11%; €49 billion), ahead of the United Kingdom (10%; €44 billion), Switzerland (6%; €28 billion), Japan and Türkiye (each 3%; €15 billion and €14 billion, respectively).
Pharmacy made up the largest share (30%) of overall high-tech exports to non-EU countries, with the United States being the top partner. Electronics-telecommunications (20%) and aerospace (18%) followed, with China and the United States as the leading partners in these sectors respectively.
Source dataset: DS-018995; Eurostat extraction
Pharmacy was the largest exported category for Switzerland, the United States (both 48% of high-tech exports; €14 billion and €61 billion, respectively), and Japan (39%; €6 billion).
The largest category for China (31% of high-tech exports to China; €15 billion) and the United Kingdom (22%; €10 billion) was electronics-telecommunications. For Türkiye, it was aerospace (35%; €5 billion).
Source: Eurostat
Legal Notice: The information in this article is intended for information purposes only. It is not intended for professional information purposes specific to a person or an institution. Every institution has different requirements because of its own circumstances even though they bear a resemblance to each other. Consequently, it is your interest to consult on an expert before taking a decision based on information stated in this article and putting into practice. Neither Karen Audit nor related person or institutions are not responsible for any damages or losses that might occur in consequence of the use of the information in this article by private or formal, real or legal person and institutions.